For textile manufacturers, the right dyeing method is essential to achieve aesthetics, durability and sustainability. Some important dye types are natural, synthetic, reactive and vat dyes.
We will discuss all these types and their applications in the textile industry. We’ll also look into key dyeing methods such as batch, continuous and garment industrial fabric dyeing methods with cost and environmental impact.
Let’s find out how Colourinn Auxiliaries provides tailored solutions for your textile production.
Why Dyeing Matters in Textile Manufacturing
Dyeing changes raw textiles into colourful, functional products meeting consumer demands for style and performance.
And it is not just colour; colour fastness, durability & functionality are important issues in fashion & home textiles as well as industrial fabric dyeing.
Proper dyeing in the textile industry improves market acceptance, durability and fulfils sustainability objectives by lowering environmental impact (by lowering water as well as chemical consumption).
Understanding Dye Types
The right choice of dye is the basis of successful dyeing. Some dyes work better in particular fibers or applications to achieve particular color fidelity and durability. Breakdown of Dye Types:
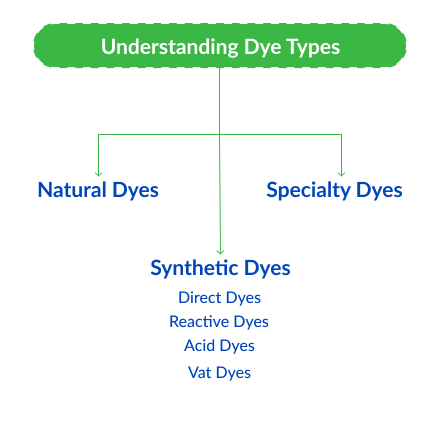
Natural Dyes
Extracted from plants, insects or minerals, natural dyes like indigo and madder are eco-friendly but less vibrant and less colourfast. They’re good for artisanal or sustainable brands, but less scalable for large-scale industrial fabric dyeing applications.
Synthetic Dyes
Developed since the 19th century, these types of dyes have a wide color range and high fastness. Types include:
- Direct Dyes: Simple application, best for cellulose fibers like cotton. They are economical but tend to fade.
- Reactive Dyes: Form chemical bonds with fibers – very good color fastness for cotton, wool, and blends.
- Vat Dyes: It is insoluble in water and must be reduced for application. For cotton and linen – unrivaled durability.
- Acid Dyes: Perfect for proteins like wool and silk – bright colours with strong bonding.
| Dye Type | Fiber Suitability | Pros | Cons |
| Natural | Cotton, Wool | Eco-friendly | Limited color range, less durable |
| Direct | Cotton, Rayon | Cost-effective, easy to apply | Moderate fastness |
| Reactive | Cotton, Wool | High color fastness | Requires precise conditions |
| Vat | Cotton, Linen | Excellent durability | Complex application |
Specialty Dyes
In industrial fabric dyeing, speciality dyes like disperse (for polyester) and sulfur (for cotton) are used for UV resistance or flame retardancy – important for technical textiles.
Key Dyeing Methods
Dyeing process in textile industry differs by method according to production stages and results. The right method depends on fiber type, production scale and finish.
Batch Dyeing
Batch dyeing involves dipping textiles in a dye bath – great for small to medium runs.
- Beck Dyeing: Fabric moves in rope form through a dye bath – good for long fabric runs.
- Jig Dyeing: For woven fabrics, the fabric passes through a full-width dye bath so that the color is even.
- Jet Dyeing: Use high-pressure dye liquor to circulate fabric – great for synthetic fibers at high temperatures.
Batch methods are flexible but very water-intensive – 5-10 times the fabric weight in water.
Continuous Dyeing
High volume production requires continuous industrial fabric dyeing in one pass through a dye solution. Methods include:
- Pad Dyeing: Fabric passes through a dye bath and rollers.
- Solution Dyeing: The pigments are added to polymer solutions before fibre extrusion, enabling better colour fastness for synthetics.
Continuous methods are effective in reducing water and energy use but need considerable investment in machinery.
Garment Dyeing
Garment dyeing colours whole garments, flexible to fit into current trends. Less common in industrial fabric dyeing but common for small-batch, trendy apparel.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Dyeing Process
Selecting the right dyeing method involves weighing several factors to align with production goals and market demands.
Fiber Type
Fibre type affects dye and method choice. Cellulose fibers like cotton and rayon work well with reactive or direct dyes, and protein fibers like wool and silk work well with acid dyes.
Synthetic fibers like polyester require disperse dyes and high temperature methods like jet dyeing.
Production Scale
Small batches gain flexibility from batch dyeing, and large scale operations gain efficiency from continuous industrial fabric dyeing.
Take into consideration production volume to optimise costs and turnaround time.
Colour Fastness Requirements
For fabrics that will be exposed to sunlight or frequent washing, such as automotive fabrics or sportswear, use fastidious dyes such as vat or reactive dyes.
Fastness is rated 1-8 for light and 1-5 for washing by the American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC).
Environmental Impact
Dyeing of textiles is a water- and chemical-intensive process. Green methods such as solution dyeing or digital printing save up to 90% of water.
With fluorine-free auxiliaries and natural dyes, environmental harm is also reduced.
Cost and Efficiency
Natural dyes and synthetic dyes are economical but may require wastewater treatment. For big runs, continuous dyeing lowers operational costs but involves significant initial investment.
How to Ensure Quality in Dyeing
Consistent, quality dyeing takes care of details:
- Pre-Treatment: Remove impurities from fabrics to permit uniform dye absorption.
- Auxiliaries: Leveling and wetting agents promote dye penetration and dye color uniformity.
- Testing: Fastness tests (e.g. AATCC standards) for color durability against light, washing and perspiration are performed.
- Process Control: Monitor temperature, pH & dye concentration to avoid localised dyeing.

Colourinn’s Commitment to Excellence in Dyeing
At Colourinn Auxiliaries we understand that choosing the right dyeing process in the textile industry is very important to produce vibrant, durable and sustainable textiles.
Dye types, methods and considerations from reactive dyes for cotton to eco-friendly digital printing are described.
Our expertise helps you achieve a balance between aesthetics, functionality and environmental responsibility.
Want to refresh your textiles with industrial fabric dyeing quality? Get in touch with Colourinn auxiliaries to learn more about our new dyes and Auxiliaries.
Learn how we can improve your production with custom-made, sustainable and vibrant solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. Which dyes are best for cotton fabrics?
A. Reactive and vat dyes are most effective for cotton due to their high color fastness and durability. Direct dyes are also used for economical applications, but offer lower fastness.
Q2. What is the role of auxiliaries in dyeing?
A. Auxiliaries like levelling agents and wetting agents ensure even dye distribution, enhance dye penetration, and improve overall dyeing quality and consistency.
Q3. Why is dyeing important in textile manufacturing?
A. Dyeing transforms raw fabrics into colorful, functional textiles. It enhances product appeal, durability, and color fastness while supporting sustainability by optimising water and chemical usage.

